-
Undertake a Risk Assessment
A comprehensive risk analysis is essential to understand the specific threats within the organisation’s loading dock. Taking a walk around the space and considering what employees will be doing day-to-day can quickly highlight potential dangers. Do walkways guide workers and visitors around the space safely? Are floors kept clear? Are handrails in place? The HSE recommends a comprehensive list of questions, on their Site Safety, Loading Areas webpage.
Looking at any recent health and safety incidents will also highlight problems and get a better employee perspective.
- What tasks are they struggling to complete safely?
- Are the same injuries occurring frequently?
Having determined current safety issues, the next step is to introduce appropriate mechanical solutions for safety, warning signs, training, and electrical safety.
-
Set Automation Priorities
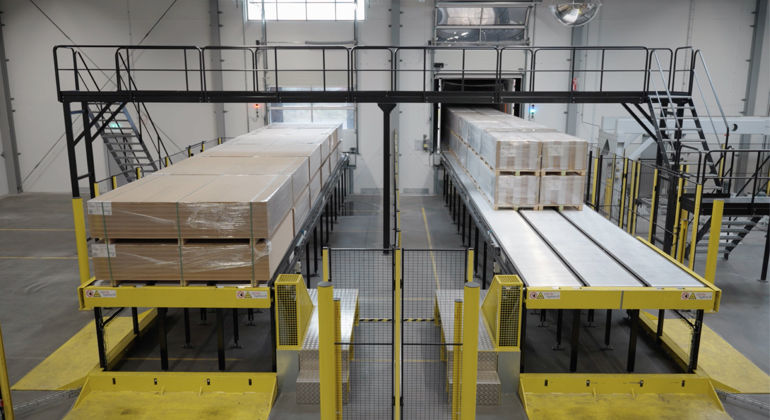
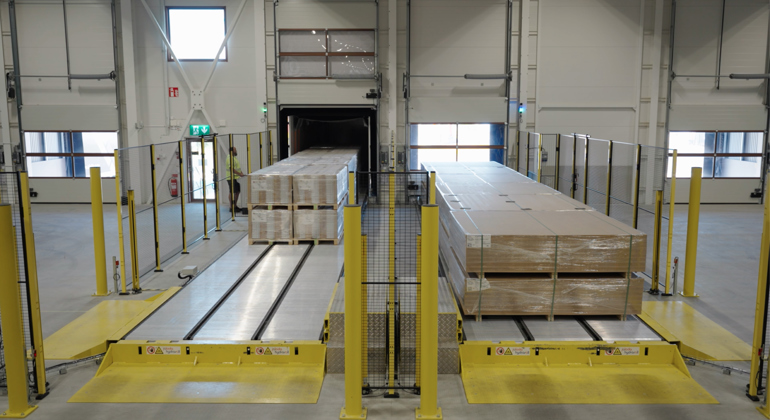
The risk assessment will highlight the key areas of business risk, allowing a business to set automation priorities. The next step is to gauge whether the business would benefit from an automated loading system. A standard viability questionnaire will help to ascertain whether a business would benefit from automation, the type of loading solution that would best suit their requirements, and how they should approach prioritising automation.
The questionnaire covers key issues, including:
Current unloading and loading processes:
- Type of loads (for example, pallets) – material, weights and size.
- Hours of operation, number of employees involved and the daily shift pattern.
- Inbound and outbound pallet flow volumes, on a daily, weekly, monthly and annual basis, and a forecast of how the business will scale (if this is a bottleneck).
- Equipment currently used – such as forklifts and electric stackers.
- Loading processes – for example, from the ground, the side or through rear doors.
- Type and size of trailer(s).
- Trailer routes and distances.
Business issues arising from the current manual process, including:
- Accidents and/ or ‘near misses’.
- Time taken to load/ unload.
- Driver waiting times.
- Limitation on growth due to manual processes.
- Demand to reduce loading times.
- Damage to goods or equipment.
- Space limitations.
This information provides vital insight to support a business case for automation and fine-tune the right automated loading system.